Differentiation, transformation and regeneration of the intestinal epithelium
The gut comprises three entities: the epithelium, the mucosal immune system and the commensal flora. Preservation of intestinal homeostasis is achieved through a balance of intestinal integrity, anti-inflammatory and inflammatory response and diverse composition of bacteria. This balance is skewed in intestinal disorders and system conditions. It breaks the alliance between the host and the bacterial colonizers, resulting in a selection of virulent pathogens, dysbiosis and a robust and maladaptive inflammatory, anti-inflammatory response.
a. The therapeutic potential of TNK1-targeting in the reconstruction of the impaired intestinal barrier in sepsis
Sepsis is a complex systemic disease that occurs due to a dysregulated host response to infection and is characterized by difficulty in diagnosis, high morbidity and mortality. A greater understanding of how trauma and gut failure lead to sepsis and progression to MODS is needed. We have shown that thirty-eight-negative kinase 1 (TNK1) promotes intestinal barrier breach, followed by septic shock and multi-organ dysfunction. Our work suggests TNK1 as a potential therapeutic target to prevent sepsis and MODS. TNK1 is an essential player development and functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The TNK1 expression pattern is modulated to maintain the development and growth of the GT during embryonic development and intestinal regeneration in adults. We aim to investigate whether TNK-targeting strengthens the intestinal epithelial barrier and prevents increased permeability in response to sepsis. To address this, we use a mouse model with intestine-specific loss of TNK1. Targeting of TNK1 holds translational potential for clinical treatments of patients. Therefore, we also evaluate the TNK1 kinase targeting by pharmacological intervention.
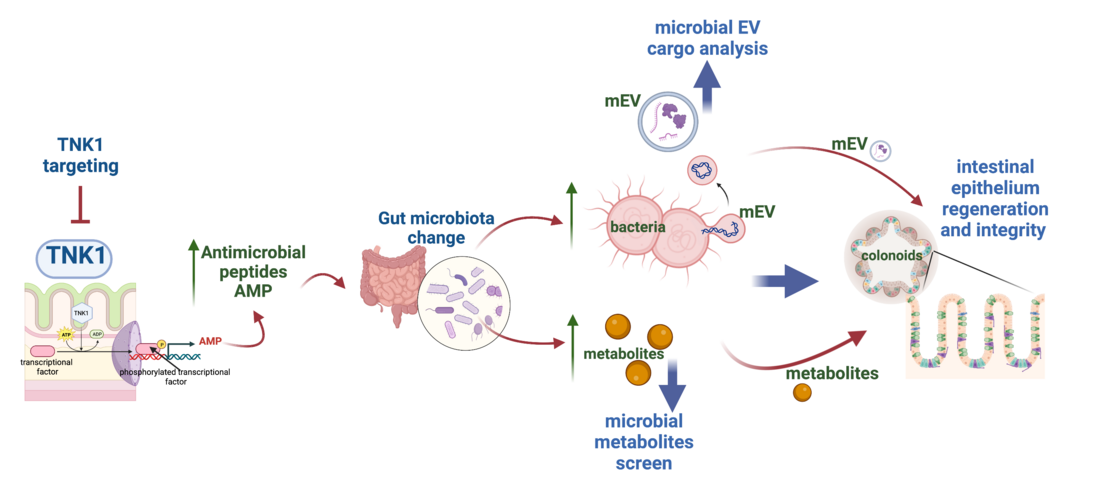
b. TNK1 in microbiota-host interaction mediated via microbial products.
The microbiota has a mutualistic relationship with the host and influences many physiological functions, often by shaping the mucosal immune system. Differences in the microbiota composition contribute to variability in immune responses and disease susceptibility and outcome, especially in immunological conditions. Understanding what decides microbiome composition is the prerequisite for developing a microbiome-targeted therapy. Intestinal mucosa harbours a unique microbial community of central importance for the mutualistic relationship between the host and its microbiota. Our group deciphers how TNK1 kinase impacts the composition of mucosa-associated microbiota and its interplay with mucosa via microbial extracellular vesicles (mEVs) and metabolites. We will apply in vivo, and ex vivo approaches, specifically the 3D culture of colonoids, to evaluate the regulatory roles of mEVs from TNK1-KO mice on epithelial regenerative functions.
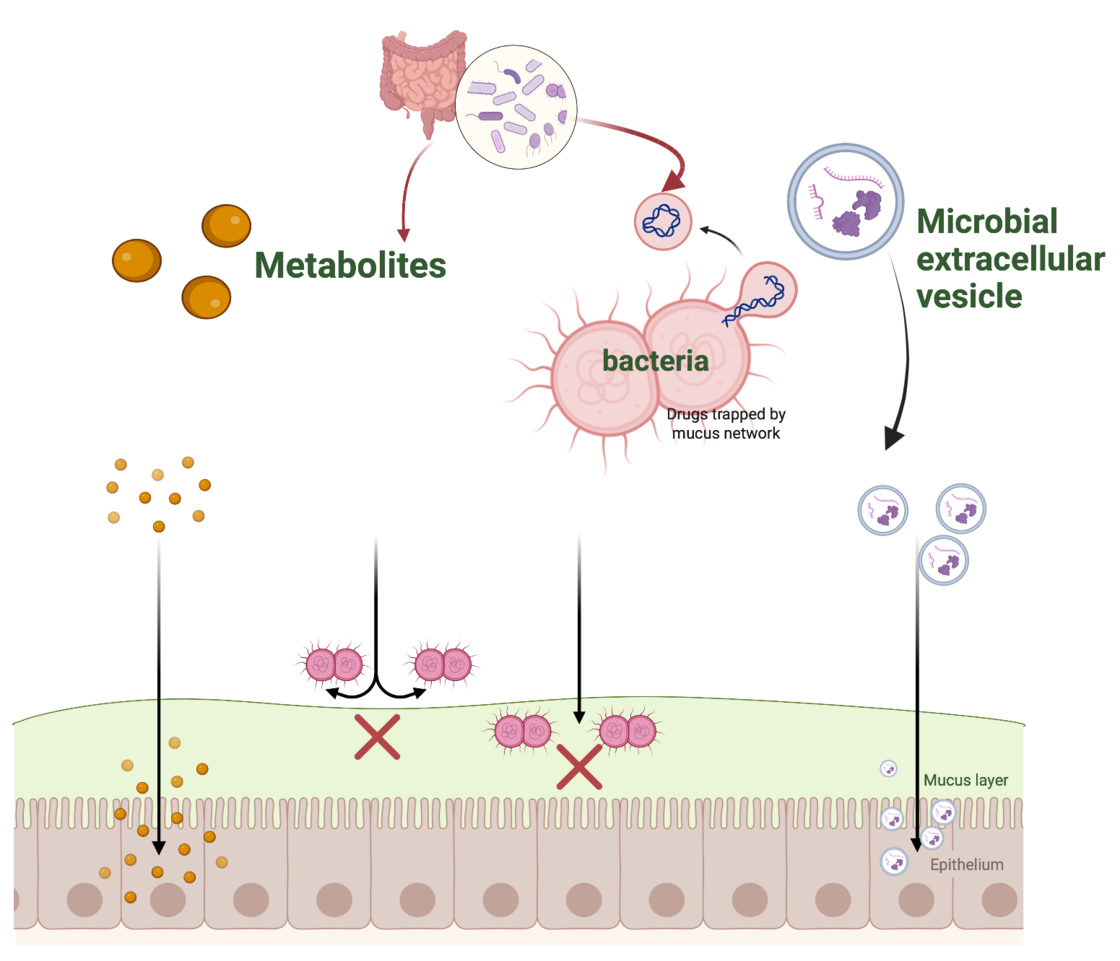
C. Evaluation of microbiota-intestine crosstalk mediated by bacterial extracellular vesicles
Maintenance of intestinal homeostasis depends on complex interactions between the host epithelium and the commensal microbiota. To date, there is only scarce data regarding the physiological relevance of small extracellular vesicles (sEV) expelled from commensal bacteria. Evidence suggests that they serve as important transmitters to modulate the response of innate immune cells, thereby contributing to a mitigation of intestinal inflammation in several in vivo studies. To date, the underlying mechanisms of action are largely unknown and object of ongoing research.
This project aims at investigating a potential beneficial impact of sEV derived from the probiotic species Limosilactobacillus reuteri and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on acutely challenged colonic epithelium ex vivo. To study the impact of microbial sEVs on the host epithelium we use colonic organoids generated from an inducible Tnk1-overexpressing mouse line. We are particularly interested in examining a potential interference of the bacterial sEV with barrier integrity and permeability.
Pancreatic Cancer and Gut Microbiome
Gut microbiota plays a significant role in the human body providing many beneficial effects on the host. However, its dysbiotic alterations may affect the tumorigenic pathway and then trigger the development of pancreatic cancer. This dysbiosis can also modulate the aggressiveness of the tumor, influencing the microenvironment..
PKD1 & Microiota
Postdoc / Principal Investigator
Current group members

Dr. med. Viktoria Hentschel
Fachärztin für Innere Medizin und Gastroenterologie, derzeit in Elternzeit
Schwerpunkte
Chronisch-entzündliche Darmerkrankungen, Derzeit Elternzeit







Yasmin Witzigmann
BSc Student
Schwerpunkte
Intestinal Organoids

Claudia Längle
Technical Assistant, CTA


Cooperation Partners
- Prof. Josh Andersen, University Of Utah, USA
- Prof. Matthias Meier, Helmholtz Zentrum München , Germany
- Prof .Johan van Lint, KA Leuven, Belgium
- Dr. Mohamed Ali Jarboui, University of Tübingen, Germany
- Prof. Dr. med. Karl-Herbert Schäfer, Working Group Enteric Nervous System, University of Applied Sciences Kaiserslautern (Campus Zweibrücken)
- Prof. Dr. Markus Egert, Microbiology & Hygiene Group, University Furtwangen
- Prof. Dr. Martin von Bergen, Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research UFZ, Dep. Of Molecular Toxicology, Leipzig
In situ sensing physiological properties of biological tissues using wireless miniature soft robots.
Wang C, Wu Y, Dong X, Armacki M, Sitti M.Sci Adv. 2023 Jun 9;9(23):eadg3988. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg3988. Epub 2023 Jun 7.PMID: 37285426
Endothelial Protein kinase D1 is a major regulator of post-traumatic hyperinflammation
Jonathan Schönfelder 1, Tanja Seibold 1, Mareen Morawe 1, Robert Sroka 1, Nora Schneider 1, Jierui Cai 1, Josip Golomejic 1, Lena Schütte 1, MilenaArmacki 1, Markus Huber-Lang 2, Miriam Kalbitz 3, Thomas Seufferlein 1, Tim Eiseler 1Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 2, doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1093022.
Small Extracellular Vesicles Propagate the Inflammatory Response After Trauma.
Seibold T, Schönfelder J, Weeber F, Lechel A, Armacki M, Waldenmaier M, Wille C, Palmer A, Halbgebauer R, Karasu E, Huber-Lang M, Kalbitz M, Radermacher P, Paschke S, Seufferlein T, Eiseler T.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Oct 28:e2102381. doi: 10.1002/advs.202102381.
Intestinal organoids in co-culture: Redefining the boundaries of gut mucosa ex vivo modeling
Hentschel V, Seufferlein T, Armacki M. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 Oct 13. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00043.2021. Online ahead of print.PMID: 34643092
Protein Kinase D1, Reduced in Human Pancreatic Tumors, Increases Secretion of Small Extracellular Vesicles From Cancer Cells That Promote Metastasis to Lung in Mice.
Armacki M@, Polaschek S @, Waldenmaier M ,Morawe M,Ruhland C, Schmid R, Lechel A, Tharehalli U, Christoph S, Bektas Y, Li H, Kraus JM, Kestler HA, Kruger S, OrmannsS, WaltherP, Eiseler T$ and Seufferlein T1$.Gastroenterology in press 2020. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.052 (@ equal contribution, $ shared senior author).
Thirty-eight-negative kinase 1 mediates trauma-induced intestinal injury and multi-organ failure.
Armacki M, Trugenberger AK, Ellwanger AK, Eiseler T, Schwerdt C, Bettac L, Langgartner D, Azoitei N, Halbgebauer R, Groß R, Barth T, Lechel A, Walter BM, Kraus JM, Wiegreffe C, Grimm J, Scheffold A, Schneider MR, Peuker K, Zeißig S, Britsch S, Rose-John S, Vettorazzi S, Wolf E, Tannapfel A, Steinestel K, Reber SO, Walther P, Kestler HA, Radermacher P, Barth TF, Huber-Lang M, Kleger A, Seufferlein T. J Clin Invest. 2018 Nov 1;128(11):5056-5072. doi: 10.1172/JCI97912. Epub 2018 Oct 15. PMID: 30320600; PMCID: PMC6205400.
Thirty-Eight-Negative Kinase 1 Is a Mediator of Acute Kidney Injury in Experimental and Clinical Traumatic Hemorrhagic Shock.
Halbgebauer R, Karasu E, Braun CK, Palmer A, Braumüller S, Schultze A, Schäfer F, Bückle S, Eigner A, Wachter U, Radermacher P, Resuello RRG, Tuplano JV, Nilsson Ekdahl K, Nilsson B, Armacki M, Kleger A, Seufferlein T, Kalbitz M, Gebhard F, Lambris JD, van Griensven M, Huber-Lang M.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 26;11:2081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02081. eCollection 2020.
STK33 participates to HSP90-supported angiogenic program in hypoxic tumors by regulating HIF-1/VEGF signalling pathway.
Liu Y, Steinestel K, Rouhi A, Armacki M, Diepold K, Chiosis G, Simmet T, Seufferlein T, Azoitei N*. Oncotarget 2017, 8(44):77474-77488.
Protein kinase D2 induces invasion of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating matrix metalloproteinases.
Wille C, Köhler C, Armacki M, Jamali A, Gössele U, Pfizenmaier K, Seufferlein T*, Eiseler T*. Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Feb;25(3):324-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-06-0334. Epub 2013 Dec 11. PMID: 24336522; PMCID: PMC3907273 .
A novel splice variant of calcium and integrin-binding protein 1 mediates protein kinase D2-stimulated tumour growth by regulating angiogenesis.
Armacki M, Joodi G, Nimmagadda SC, de Kimpe L, Pusapati GV, Vandoninck S, Van Lint J, Illing A, Seufferlein T. Oncogene. 2014. Feb 27;33(9):1167-80. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.43.
Keratin 8 phosphorylation regulates keratin reorganization and migration of epithelial tumor cells.
Armacki M, Busch T, Eiseler T, Joodi G, Temme C, Jansen J, von Wichert G, Omary MB, Spatz J, Seufferlein T. J Cell Sci. 2012 May 1;125(Pt 9):2148-59. doi: 10.1242/jcs.080127. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PMID: 22344252; PMCID: PMC3367938.
Protein Kinase D2 Is an Essential Regulator of Murine Myoblast Differentiation.
Alexander Kleger, Christiane Loebnitz., Ganesh V. Pusapati, Milena Armacki, MartinMuller, Stefan Tumpel, Anett Illing, Daniel Hartmann, Cornelia Brunner, StefanLiebau, Karl L. Rudolph, Guido Adler1, Thomas Seufferlein. PLOS One 2011
Role of the Second Cysteine-Rich Domain and Pro275 in Protein Kinase D2 Interaction with ADP-Rybosylation Factor 1, Trans-Golgi Network Recruitment, and Protein Transport
Ganesh Varma Pusapati,* Denis Krndija,* Milena Armacki,† Gotz von Wichert,*
Julia von Blume,‡ Vivek Malhotra,‡ Guido Adler,* and Thomas Seufferlein. Molecular Biology of the Cell.2010
Characterization of cortactin as an in vivo protein kinase D substrate: Interdependence of sites and potentiation of Src.
L. de Kimpe, K. Janssens, R. Derua, M.Armacki, S. Goicoechea, C. Otey, E. Waelkens, S. Vandoninck, J.R. Vandenheede, T. Seufferlein, J.van Lint. Cellular Signalling 2009
Thirty-eight-negative kinase 1 (TNK1) facilitates TNF-induced apoptosis by blocking NF-kB activation
Ninel Azoitei, Andreas Brey, Tobias Bush, Simone Fulda, Guido Adler, Thomas Seufferlein. Oncogene (2007), 26(45): 6536-6545
Join our group
We continuously offer MD, Master and Bachelor positions. In case you are interested please send your application to:
milena.armacki@uniklinik-ulm.de